
Bar Hold Danger: Deadly Asphyxiation Risk
What is a Bar Hold?
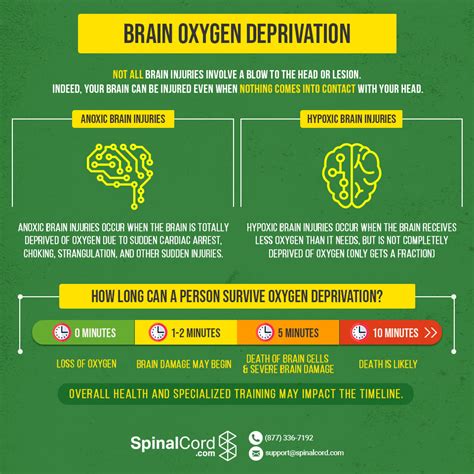
The "bar hold" refers to a dangerous breath-holding challenge where individuals restrict airflow to induce a brief state of unconsciousness. Often performed in pools or water, participants attempt to hold their breath until they pass out, believing it to be a harmless adrenaline rush. However, this game carries severe risks of hypoxia and asphyxiation, especially when combined with water environments.
The Tragic Carnival Cruise Incident
A recent case underscores the lethal potential of this challenge. A teenager was found unresponsive aboard a Carnival Cruise ship, later pronounced dead from asphyxiation linked to a bar hold. Medical experts confirm that prolonged breath-holding can cause oxygen deprivation to the brain, leading to irreversible damage or death within minutes. Water significantly heightens risks, as loss of consciousness often results in drowning.
Why Bar Holds Are Especially Dangerous
Unlike typical breath-holding exercises, bar holds involve deliberate oxygen deprivation until fainting occurs. Key dangers include:
- Hypoxic blackout: Sudden loss of consciousness without warning signs.
- Water aspiration: Inhaling water during unconsciousness.
- Brain damage: Even brief oxygen deprivation can cause neurological harm.
- Risk escalation: Competitive dares often encourage participants to push limits.
"Bar holds aren't games—they're Russian roulette with oxygen. The body's warning signals can be bypassed, making drowning or brain injury inevitable in water settings."
Warning Signs and Prevention
Parents and educators should watch for teens discussing "breath-holding games" or "fainting challenges." Prevention strategies include:
- Educate about risks: Clearly explain physiological dangers of oxygen deprivation.
- Supervise aquatic activities: Enforce constant adult monitoring near water.
- Promote safe alternatives: Encourage breath-holding only under medical guidance.
- Monitor online challenges: Discuss viral trends that glorify risky behaviors.
Medical Perspective on Asphyxiation
Asphyxiation occurs when the body is deprived of oxygen. During bar holds, carbon dioxide buildup triggers the urge to breathe, but participants override this reflex. If submerged, water prevents inhalation during blackout, leading to drowning or cardiac arrest. Recovery is possible only with immediate CPR and oxygen therapy.
What Happens After Such Tragedies?
In the Carnival Cruise case, investigations focus on whether proper safety protocols were followed. Cruise lines are reviewing onboard supervision and emergency response procedures. Meanwhile, families affected are advocating for broader awareness campaigns targeting teens about the deadly consequences of such challenges.

Key Takeaways
The bar hold phenomenon highlights how social media trends can normalize lethal behaviors. Understanding the science behind asphyxiation and communicating its irreversible consequences is crucial for preventing future tragedies.
Share this article
David Kim
Health and science reporter with a background in medicine. Passionate about making complex medical topics accessible.